Aging brings a series of unexpected challenges, such as slower metabolisms and an increased risk of chronic diseases. These realities impact physical, emotional, and financial well-being, reshaping life in profound ways. Let’s explore the harsh realities of aging that no one warns you about.
Slower Metabolism

As you age, your metabolism naturally slows down. This means your body burns fewer calories, making it easier to gain weight even if your diet and activity levels remain the same. Adjusting your eating habits and increasing physical activity can help manage this change.
Decreased Bone Density

Bone density peaks in your 30s and then begins to decline. This increases the risk of osteoporosis and fractures. Consuming calcium-rich foods and engaging in weight-bearing exercises can help maintain bone health.
Joint Pain and Stiffness

Aging often brings increased joint pain and stiffness, particularly in the knees, hips, and hands. This can be due to wear and tear or conditions like arthritis. Regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and physical therapy can alleviate some of these symptoms.
Loss of Muscle Mass

Sarcopenia, the loss of muscle mass and strength, begins around age 30 and accelerates after 60. Strength training and adequate protein intake are essential to combat this. Maintaining muscle mass is crucial for mobility and overall health.
Declining Vision

Presbyopia, or age-related farsightedness, typically starts in your 40s. You may also be at higher risk for cataracts, glaucoma, and macular degeneration. Regular eye exams and wearing appropriate corrective lenses can help manage these issues.
Hearing Loss

Hearing loss is a common part of aging, often due to long-term exposure to loud noises or natural degeneration. It can affect your ability to communicate and enjoy social activities. Hearing aids and assistive devices can improve your quality of life.
Memory Lapses

While not all memory issues are signs of dementia, occasional forgetfulness becomes more common as you age. Keeping your brain active through puzzles, reading, and learning new skills can help maintain cognitive function. Staying socially engaged also supports brain health.
Changes in Sleep Patterns

Older adults often experience changes in their sleep patterns, such as waking up earlier or having trouble staying asleep. This can be due to hormonal changes, medical conditions, or medications. Establishing a regular sleep routine and creating a comfortable sleep environment can help.
Decreased Skin Elasticity

With age, your skin loses collagen and elastin, leading to wrinkles and sagging. Sun exposure and smoking can accelerate this process. Using sunscreen, moisturizing regularly, and avoiding smoking can help protect your skin.
Digestive Issues
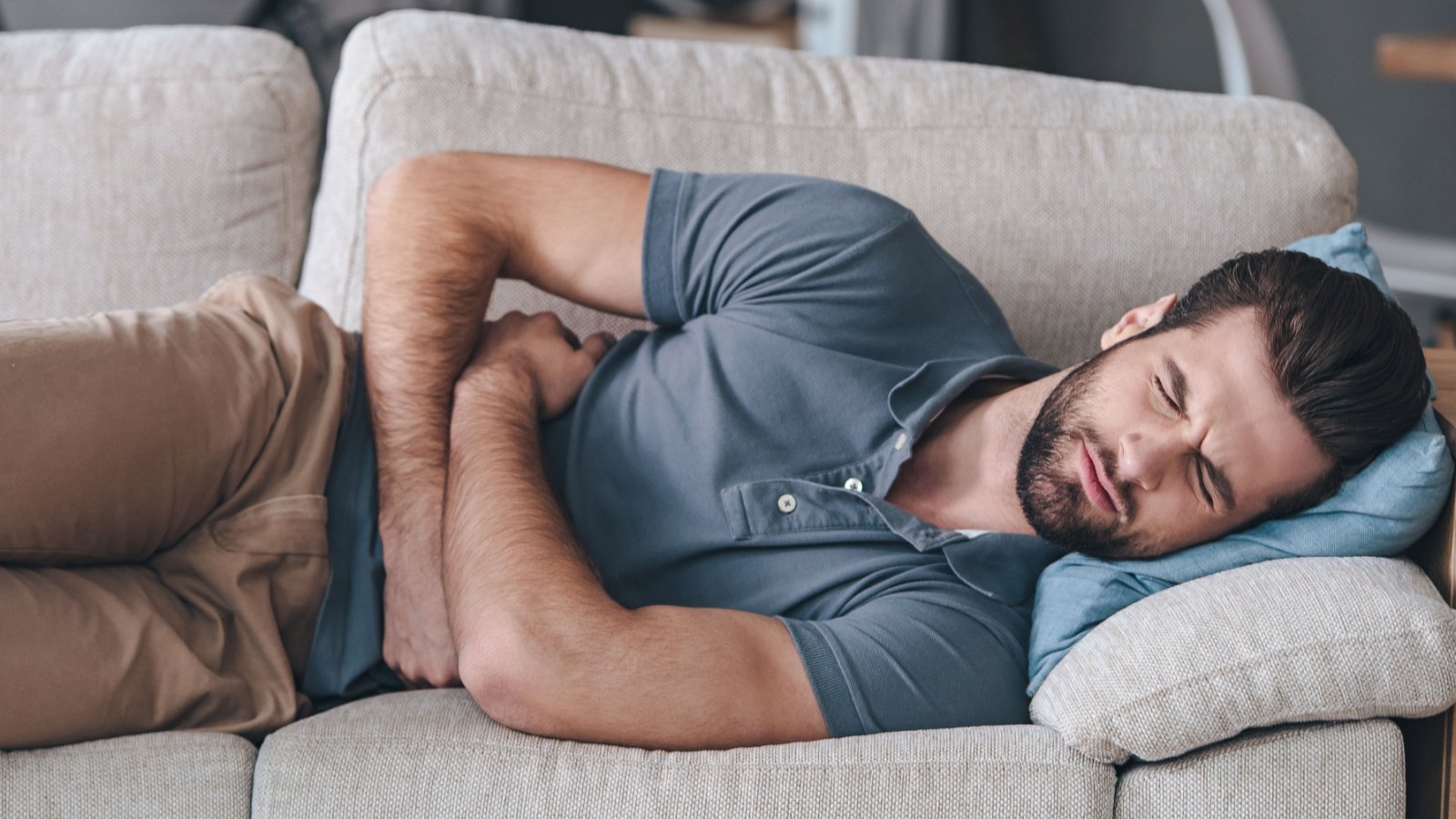

Digestive problems, such as constipation and acid reflux, become more common with age. A diet high in fiber, staying hydrated, and regular exercise can promote digestive health. Probiotics and avoiding trigger foods can also be beneficial.
Weaker Immune System

The immune system weakens with age, making you more susceptible to infections and illnesses. Vaccinations, a balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep are essential to support immune function. Frequent handwashing and avoiding sick individuals can reduce your risk.
Dental Health Decline
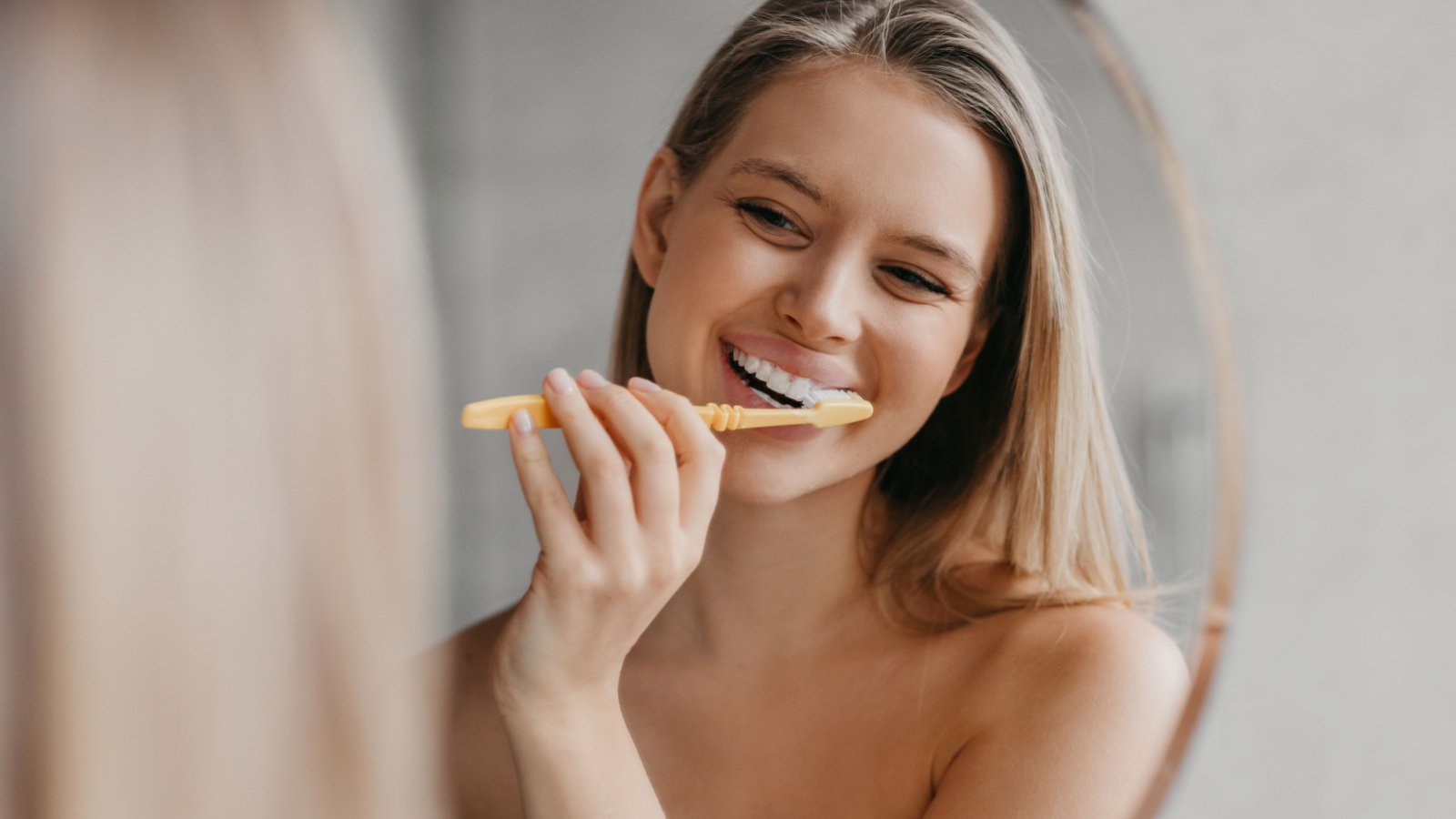

Gum disease and tooth decay are more prevalent in older adults. Regular dental checkups, brushing, and flossing are crucial to maintain oral health. A diet low in sugar and avoiding tobacco products can also help.
Decreased Sense of Taste and Smell
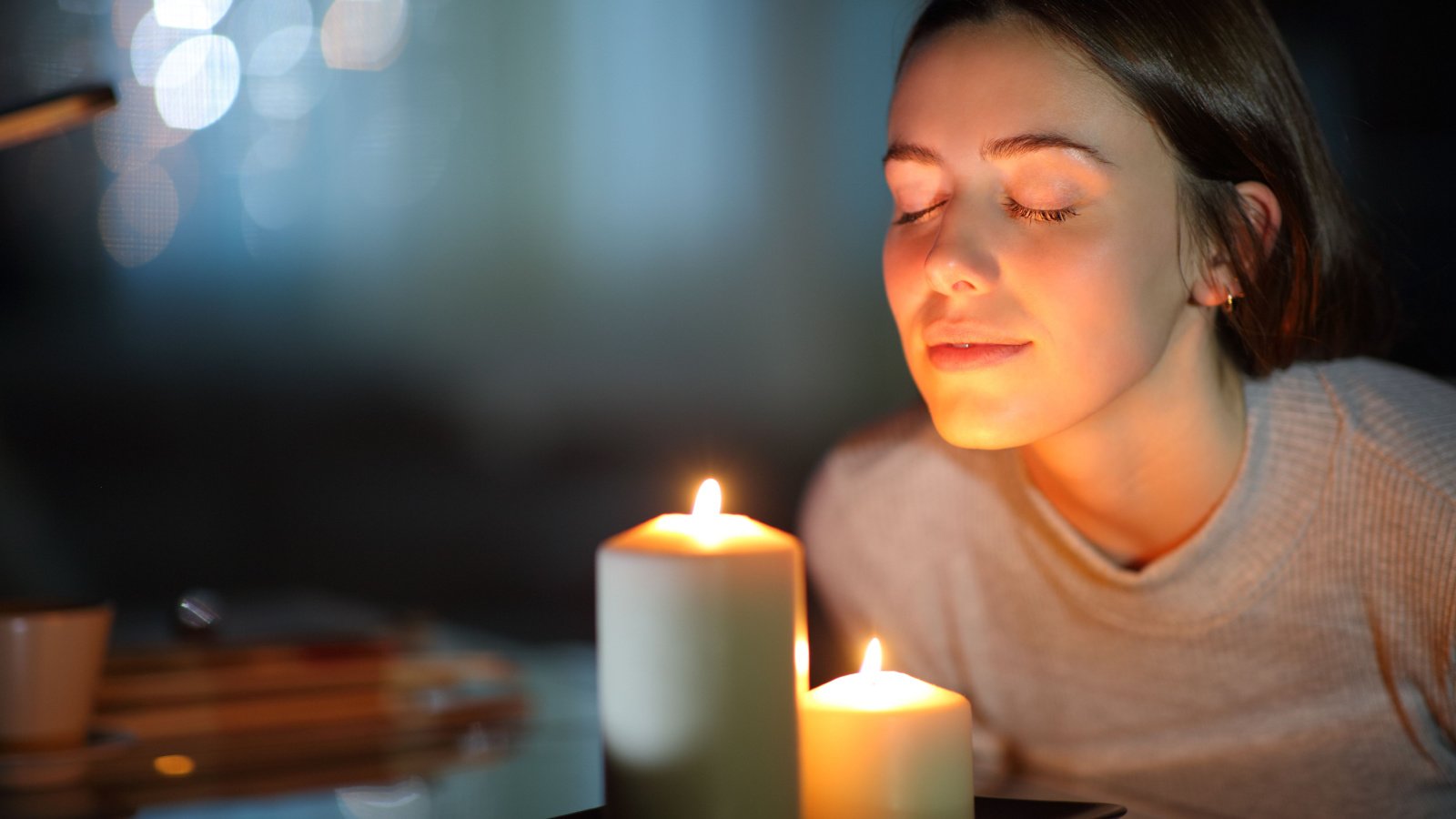

Your senses of taste and smell may diminish as you age, affecting your appetite and enjoyment of food. This can be caused by medications, illnesses, or simply aging. Enhancing flavors with herbs and spices and ensuring proper nutrition can help maintain a healthy diet.
Hair Thinning and Graying
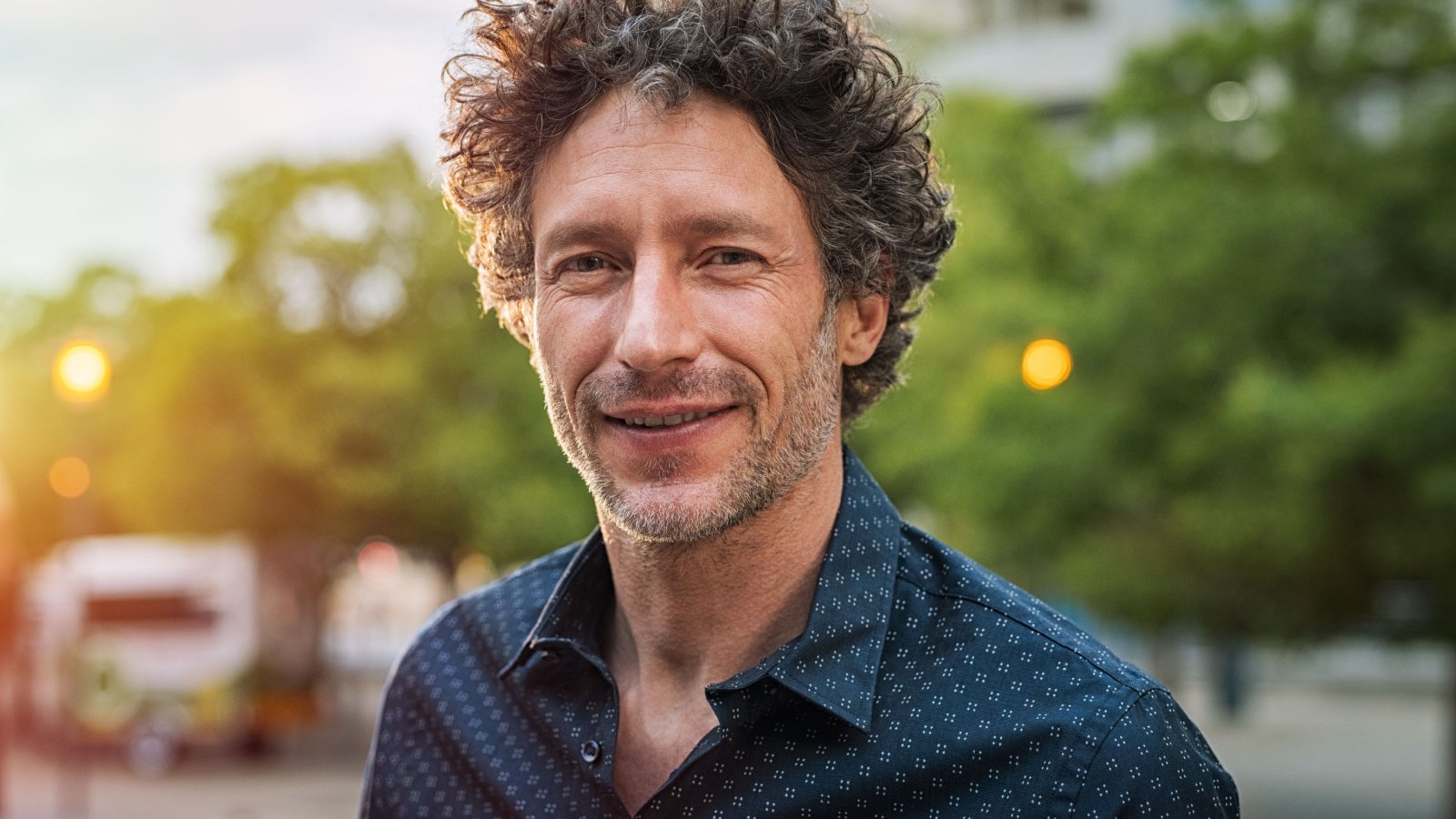

Hair naturally becomes thinner and turns gray with age. This is due to a decrease in melanin production and changes in hair follicles. A balanced diet, gentle hair care, and possibly supplements can support hair health.
Increased Risk of Chronic Diseases

Aging increases the risk of chronic conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and hypertension. Regular checkups, a healthy diet, and physical activity are vital in managing and preventing these diseases. Early detection and treatment can improve outcomes.
Balance and Coordination Issues

Balance and coordination can decline with age, increasing the risk of falls. Exercises that improve strength and balance, such as yoga and tai chi, can help. Installing handrails and removing tripping hazards in the home can also prevent falls.
Reduced Mobility

Arthritis and other joint issues can reduce your mobility over time. Staying active, managing your weight, and physical therapy can help maintain joint function. Using mobility aids when necessary can also enhance your quality of life.
Changes in Body Composition

As you age, you may notice changes in your body composition, such as increased body fat and decreased muscle mass. This can affect your metabolism and overall health. A balanced diet, strength training, and cardio exercises can help manage these changes.
Increased Fatigue

Older adults often experience more fatigue, which can be due to health conditions, medications, or lifestyle factors. Ensuring adequate rest, staying hydrated, and managing stress can improve energy levels. Consulting with a healthcare provider can help identify underlying causes.
Slower Wound Healing

The body’s ability to repair itself slows down with age, leading to slower wound healing. Proper wound care, maintaining good nutrition, and controlling underlying conditions like diabetes are crucial. Seeking medical attention for serious wounds is important.
Emotional and Mental Health Challenges

Aging can bring emotional and mental health challenges, such as depression and anxiety. Staying socially active, engaging in hobbies, and seeking professional help when needed can support mental health. Building a strong support network is also beneficial.
Decreased Flexibility

Flexibility often diminishes with age, making daily activities more challenging. Regular stretching exercises and yoga can help maintain and improve flexibility. Staying active and avoiding prolonged periods of inactivity are key to preserving joint range of motion.
Changes in Appetite

Aging can affect your appetite due to changes in metabolism, taste, and digestive function. Medications and health conditions can also play a role. Eating smaller, more frequent meals and focusing on nutrient-dense foods can help ensure adequate nutrition.
Increased Sensitivity to Temperature

Older adults often become more sensitive to temperature changes due to changes in body composition and reduced circulation. Dressing in layers, maintaining a comfortable home temperature, and staying hydrated can help manage this sensitivity.
Financial Concerns

Financial stability can become a significant concern as you age. Planning for retirement, budgeting, and seeking financial advice can help manage these concerns. It’s important to review and adjust your financial plans regularly to ensure security.







Wow! This blog looks exactly like my old one! It’s on a completely different subject but it has pretty much the same layout and design. Outstanding choice of colors!