All states carry their own set of struggles and triumphs, but some states have more unhappy citizens than other. Below we examine how local economies, culture, and healthcare contribute to the states that rank at the bottom of the health and happiness index.
Mississippi
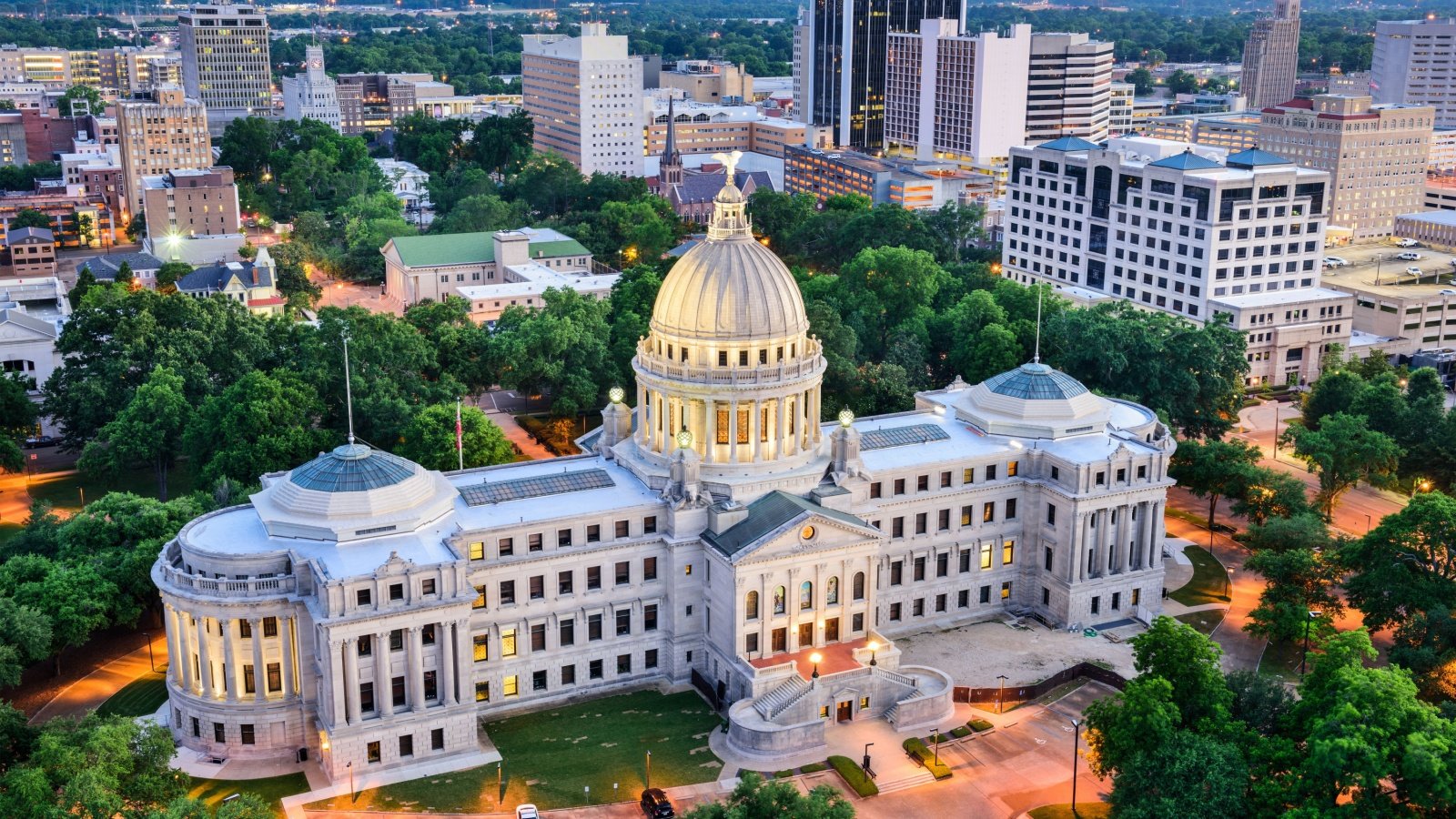

Mississippi often appears at the bottom of health and happiness rankings due to its high rates of obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. Economic challenges and limited access to quality healthcare exacerbate these issues.
West Virginia
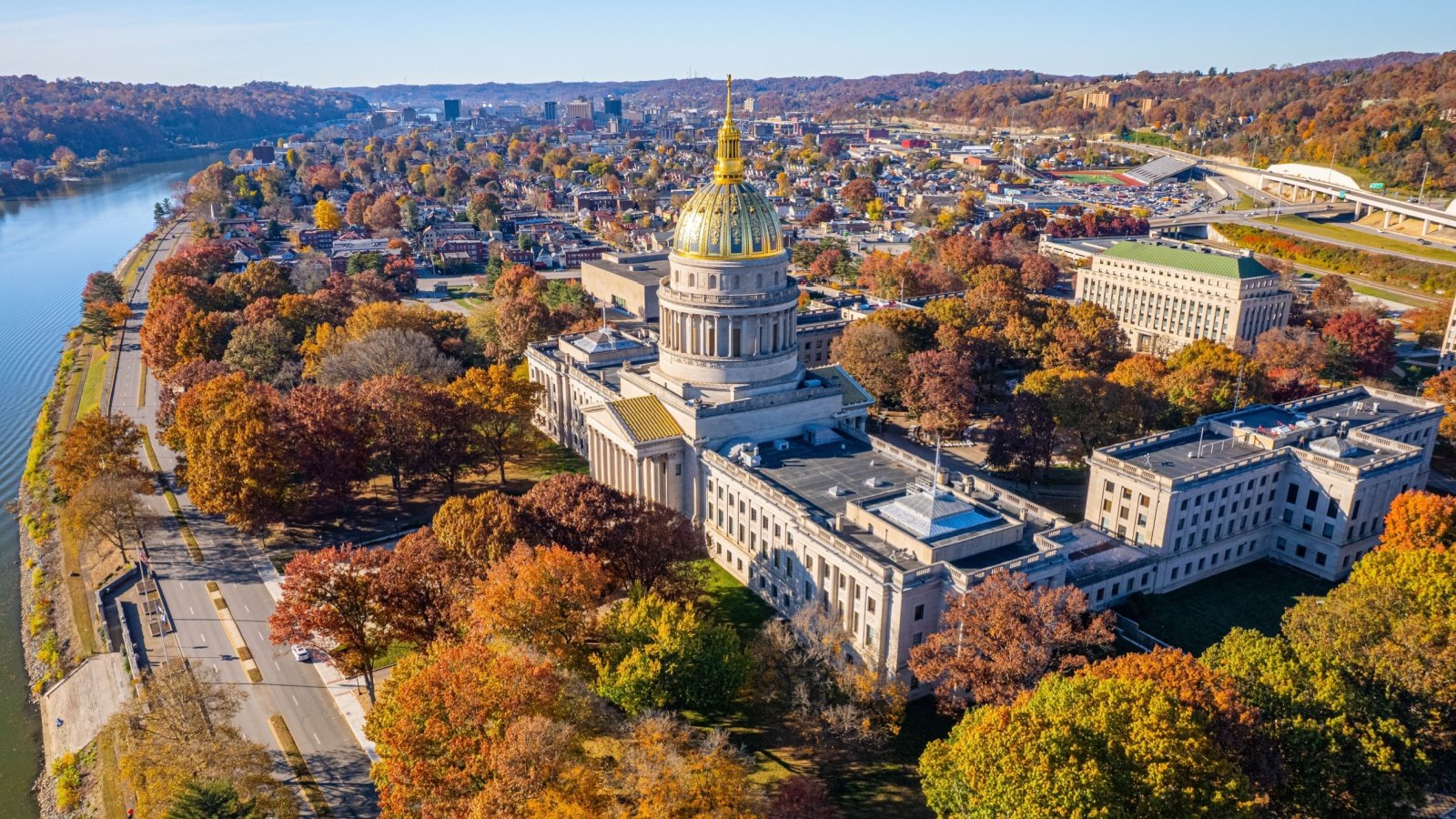

West Virginia faces significant health challenges, including high rates of smoking, obesity, and opioid addiction. The state’s economy, heavily reliant on coal mining, has also contributed to environmental health concerns.
Louisiana

Louisiana’s vibrant culture and cuisine are overshadowed by health issues such as high blood pressure and obesity. Environmental challenges, including coastal erosion and hurricanes, further impact residents’ well-being.
Arkansas

With high rates of smoking and heart disease, Arkansas’s health metrics lag behind national averages. Rural areas, in particular, suffer from a lack of healthcare facilities. However, the state’s natural beauty and community programs offer avenues for promoting healthier lifestyles.
Alabama

Alabama grapples with high obesity rates and limited access to mental health services. Economic disparities and education levels also contribute to its health challenges. Investing in healthcare infrastructure and education can help Alabama build a healthier future.
Oklahoma

Oklahoma’s health is impacted by high rates of smoking and a lack of physical activity among its residents. The state also struggles with mental health issues, with a high number of people reporting frequent mental distress.
Kentucky
Kentucky’s health challenges are marked by high smoking rates and deaths from cancer and heart disease. Economic reliance on coal mining has also affected environmental health. Community efforts to promote healthy living and diversify the economy offer hope for improvement.
Tennessee

Tennessee faces health issues such as obesity and diabetes, compounded by high rates of smoking. Access to healthcare varies significantly across urban and rural areas, affecting overall health outcomes.
South Carolina

South Carolina struggles with high obesity rates and low birth weight in newborns. Access to healthcare services in rural areas remains a challenge. Enhancing healthcare infrastructure and preventive care programs is essential for improvement.
New Mexico

New Mexico contends with high rates of alcohol-related deaths and drug overdoses. Economic factors and access to healthcare services play significant roles in these challenges. Strengthening community health programs and support systems is crucial.
Missouri

Missouri’s health metrics are affected by high rates of smoking and obesity. Urban areas, in particular, face challenges with air quality and access to healthy food options. Initiatives to promote active living and improve urban environments are underway.
Indiana

Indiana struggles with obesity and smoking, impacting its overall health rankings. Rural areas lack access to healthcare facilities, contributing to health disparities. State and community efforts to increase healthcare access and promote healthy lifestyles are key.
Ohio

Ohio faces challenges with obesity, smoking, and opioid addiction. Economic transitions from manufacturing to service sectors have also impacted community well-being. Focused efforts on health education and substance abuse prevention are critical for improvement.
Michigan

Michigan’s health is challenged by high rates of obesity and smoking, along with environmental issues in industrial areas. Economic shifts have led to disparities in health access and outcomes. Investing in public health infrastructure and community wellness programs offers a path forward.
Georgia

Georgia deals with high rates of obesity and diabetes, particularly in rural areas where healthcare access is limited. Economic inequality affects health outcomes across different communities. Expanding healthcare access and community health initiatives can help address these issues.
Nevada

Nevada faces health challenges with high rates of smoking and substance abuse. The transient nature of some of its population and reliance on the tourism industry contribute to these issues. Strengthening healthcare services and preventive care is essential for residents’ well-being.
North Carolina

Obesity and heart disease rates impact North Carolina’s health. Rural areas suffer from a lack of access to healthcare services. State-wide initiatives focused on health education and access are making strides in addressing these challenges.
Alaska

Alaska’s unique geographical challenges contribute to its health issues, including high rates of depression and substance abuse. The isolation of many communities makes access to healthcare difficult, exacerbating mental and physical health challenges.
Arizona

Arizona grapples with high rates of obesity and diabetes, partly due to lifestyle and dietary habits. Access to healthcare in rural and tribal areas presents significant challenges, affecting overall health outcomes.
Florida

Florida faces health challenges with its aging population, including high rates of chronic diseases such as heart disease and diabetes. The state also contends with mental health issues, particularly among older adults and in lower-income communities.
Pennsylvania

Pennsylvania’s industrial legacy has left some areas struggling with pollution and associated health issues, such as asthma and cardiovascular diseases. Economic disparities across urban and rural areas further complicate access to quality healthcare.
Texas

Texas contends with high obesity rates and significant healthcare access issues, especially in rural and border areas. The state’s large uninsured population affects health outcomes, making preventive care and treatment less accessible.
Illinois

Illinois faces high rates of obesity, diabetes, and respiratory diseases. Chicago, in particular, grapples with health disparities influenced by socioeconomic factors. Strengthening public health initiatives and addressing socioeconomic disparities are critical to improving health.
New York

New York’s diverse population faces urban pollution and rural healthcare access issues. Mental health is a significant concern. Comprehensive public health strategies that address both urban and rural health needs are necessary for improvement.
California

California faces high-stress levels, pollution, and homelessness. Access to healthcare varies greatly across its vast and diverse population. Targeted health initiatives and policies aimed at reducing disparities and improving access to care are crucial for the state’s overall well-being.








